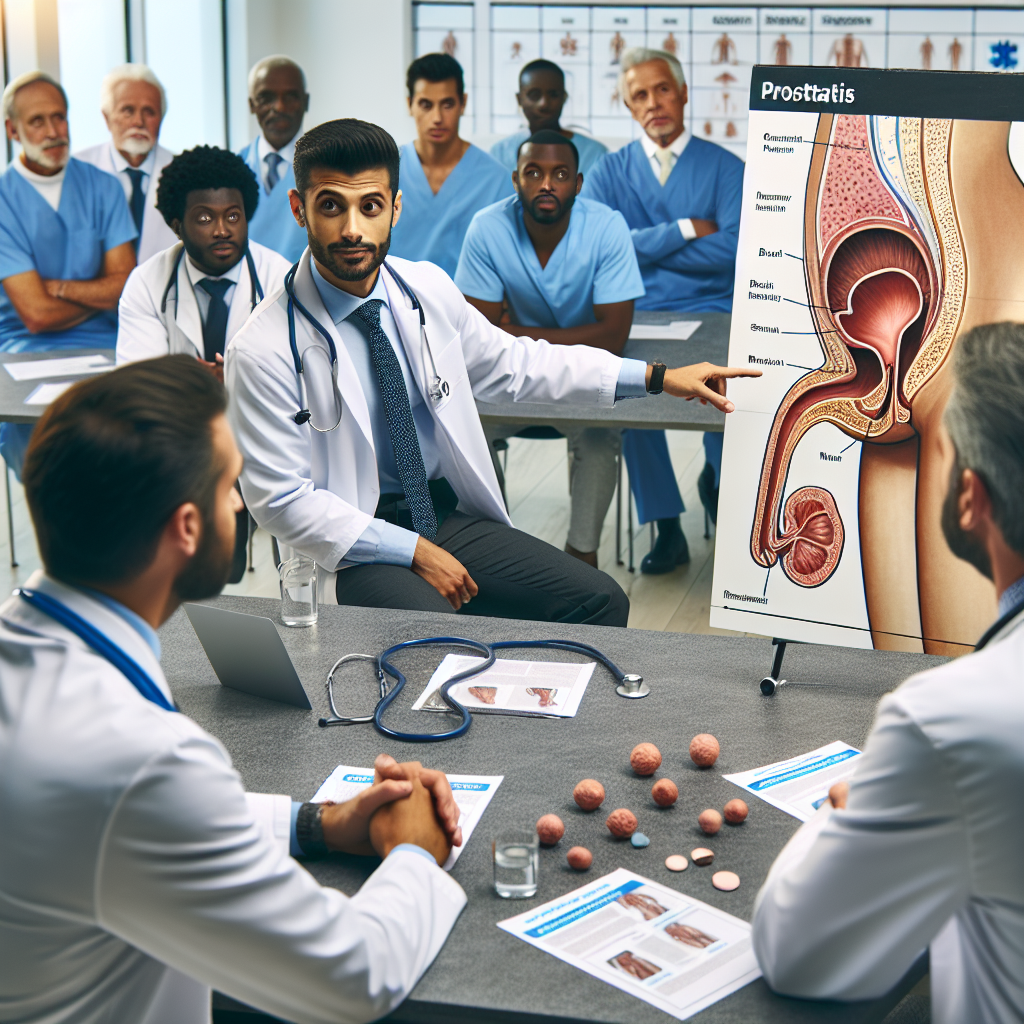
The Prevalence of Prostatitis
In terms of prevalence, prostatitis is recognized as one of the most common urological conditions in men, particularly those under the age of 50. Research suggests that approximately 5-10% of men experience symptoms of prostatitis at some point in their lives. This estimation, however, might be conservative due to the variability in symptoms and the underreporting of cases. The actual prevalence rate could be significantly higher, considering the diverse manifestation of prostatitis ranging from acute bacterial infections to chronic pelvic pain syndromes. The National Institutes of Health (NIH) classifies prostatitis into four categories: acute bacterial prostatitis, chronic bacterial prostatitis, chronic prostatitis/chronic pelvic pain syndrome (CP/CPPS), and asymptomatic inflammatory prostatitis. Among these, CP/CPPS is estimated to account for approximately 90% of all prostatitis cases, highlighting its considerable impact on men’s health. Epidemiological studies further reveal that the prevalence of prostatitis symptoms increases with age. Men aged 30-50 are more likely to report these symptoms, although cases have been documented in men of younger and older age groups as well. The geographical distribution also varies, with some regions reporting higher incidences, possibly due to better diagnostic facilities and greater awareness among healthcare professionals and patients. Understanding these statistics is fundamental for healthcare providers as it aids in early diagnosis and effective management of the condition. Furthermore, educating men about the potential prevalence and symptoms of prostatitis can encourage timely medical consultation, potentially reducing the adverse impacts on quality of life.
Different Types of Prostatitis and Their Commonality
Prostatitis manifests in several different forms, each presenting unique characteristics and affecting men to varying degrees. It’s important to understand these types to better grasp how this condition can impact individuals. The four main types of prostatitis are Acute Bacterial Prostatitis, Chronic Bacterial Prostatitis, Chronic Prostatitis/Chronic Pelvic Pain Syndrome (CP/CPPS), and Asymptomatic Inflammatory Prostatitis. Acute Bacterial Prostatitis is the least common but potentially the most severe form. It typically develops suddenly and is caused by a bacterial infection. Symptoms include fever, chills, lower back pain, and urinary difficulties. Immediate medical attention is required to manage this condition effectively. Chronic Bacterial Prostatitis, though also bacterial in origin, presents with milder symptoms compared to its acute counterpart. This form persists over a more extended period, often resulting in recurring urinary tract infections. Men with chronic bacterial prostatitis might experience discomfort or pain in the pelvic area and urinary issues that come and go over time. Chronic Prostatitis/Chronic Pelvic Pain Syndrome (CP/CPPS) is the most prevalent type, accounting for the majority of prostatitis cases. Despite its high occurrence, this form remains poorly understood, as it is not caused by a bacterial infection. Symptoms vary widely among individuals, including pelvic pain, urinary problems, and sexual dysfunction, often without any detectable infection or pathology. Asymptomatic Inflammatory Prostatitis is usually discovered incidentally during examinations for other conditions. This type does not produce noticeable symptoms but involves inflammation of the prostate. While it doesn’t directly affect quality of life, its presence may be a risk factor for other prostate issues. Understanding the diversity of prostatitis types and their prevalence can assist men and their healthcare providers in identifying the condition promptly and selecting the most effective treatment strategies.
Symptoms and Diagnosis
Prostatitis can present a range of symptoms that vary in intensity and duration. Common symptoms include pain or discomfort in the pelvic region, lower back, or genital area. In addition to pain, men may experience urinary symptoms such as frequent urination, difficulty urinating, a weak urinary stream, and a sense of urgency. Some may also suffer from sexual dysfunction, including painful ejaculation or erectile difficulties. The symptoms can be persistent, significantly affecting daily life and overall well-being. Diagnosing prostatitis can be challenging due to the overlap of its symptoms with other urological conditions. Typically, the diagnosis involves a detailed medical history and physical examination, including a digital rectal exam (DRE) to assess the prostate gland. Additional tests may include urinalysis, urine culture, and possibly imaging studies like an ultrasound or MRI to rule out other conditions. In certain cases, a prostatic massage followed by analysis of expressed prostatic secretions can help identify any bacterial infection related to chronic bacterial prostatitis. Timely and accurate diagnosis is essential for effective management and treatment.
Treatment Approaches for Prostatitis
When it comes to treating prostatitis, the approach typically depends on the type and severity of the condition. Here are some common treatment strategies used by healthcare professionals: 1. **Antibiotics**: For bacterial prostatitis, antibiotics are often the first line of treatment. The prescription could range from short-term courses to more extended regimens, particularly in cases of chronic bacterial prostatitis where longer treatments could be necessary. 2. **Alpha Blockers**: These medications help relax the muscle fibers in the prostate and bladder neck, making it easier to urinate. Alpha blockers are commonly used for chronic prostatitis/chronic pelvic pain syndrome. 3. **Anti-inflammatory Medications**: Over-the-counter pain relievers such as ibuprofen can help reduce inflammation and manage pain. In some cases, doctors may prescribe stronger anti-inflammatory medications. 4. **Physical Therapy**: Pelvic floor physiotherapy can be beneficial, especially in cases where muscle tightness contributes to the symptoms. Techniques may involve biofeedback, stretching, and specific exercises designed to relax the pelvic floor muscles. 5. **Lifestyle Modifications**: Making certain lifestyle changes, such as reducing alcohol and caffeine intake, avoiding spicy foods, and practicing stress reduction techniques, can help alleviate symptoms. Regular physical activity and adequate hydration are also recommended. 6. **Alternative Therapies**: Acupuncture, prostate massage, and the use of herbal supplements are some alternative treatments considered by some patients. While their efficacy may vary, some find these methods helpful for symptom relief. 7. **Surgery**: In rare, severe cases where other treatments have not been effective, surgical options may be considered. Procedures can range from minimally invasive surgeries to more extensive interventions to remove parts of the prostate. 8. **Counseling and Support**: Chronic pain and discomfort from prostatitis can lead to emotional and psychological stress. Counseling or support groups can provide emotional support and coping strategies for patients dealing with ongoing symptoms. By exploring these various treatment approaches, patients and healthcare providers can work together to find the most effective plan to manage prostatitis and improve quality of life.
Complications and Related Conditions
Complications and Related Conditions In cases where prostatitis is not effectively treated or managed, complications can arise, leading to significant health issues. One of the primary concerns is chronic prostatitis/chronic pelvic pain syndrome (CP/CPPS), a condition that can result in ongoing pain and discomfort. Other complications include urinary tract infections (UTIs), which can occur frequently in men with prostatitis due to bacteria entering the urinary tract during episodes of prostate inflammation. Another related condition is benign prostatic hyperplasia (BPH), which is an enlargement of the prostate gland. While BPH itself is not directly caused by prostatitis, the inflammation and irritation from prostatitis can aggravate symptoms of BPH, such as difficulty urinating or frequent urination, especially at night. Epididymitis, an inflammation of the epididymis, can also be a complication of prostatitis. This condition causes swelling and pain in the testicles and can lead to more severe issues like infertility if not treated promptly. Additionally, men with chronic prostatitis may experience sexual health problems, including erectile dysfunction (ED) and reduced libido. Psychological effects, such as anxiety and depression, are not uncommon, as ongoing pain and urinary symptoms can significantly impact mental well-being. Understanding these potential complications and related conditions underscores the importance of early diagnosis and comprehensive management of prostatitis. Healthcare providers play a crucial role in identifying these issues early and adopting a holistic treatment approach to mitigate long-term health consequences.
Managing Prostatitis: Lifestyle and Long-term Care
Quản lý Viêm Tuyến Tiền Liệt: Lối Sống và Chăm Sóc Dài Hạn Quản lý lối sống và chăm sóc dài hạn là những yếu tố quan trọng trong việc xử lý viêm tuyến tiền liệt. Đối với nhiều bệnh nhân, thay đổi lối sống có thể giúp giảm triệu chứng và cải thiện chất lượng cuộc sống. Dưới đây là một số lời khuyên lối sống và biện pháp chăm sóc dài hạn mà người bị viêm tuyến tiền liệt có thể áp dụng: 1. **Dinh dưỡng hợp lý:** Ăn uống lành mạnh có thể giúp duy trì một cơ thể khỏe mạnh và giảm viêm. Hạn chế thực phẩm có thể kích thích tuyến tiền liệt như cà phê, rượu, và thực phẩm cay hoặc chua. 2. **Tập thể dục thường xuyên:** Tập thể dục không chỉ giúp duy trì cân nặng lý tưởng mà còn cải thiện tuần hoàn máu và sức khỏe tổng thể. Những hoạt động nhẹ nhàng như đi bộ, bơi lội hoặc tập yoga có thể mang lại lợi ích. 3. **Giảm căng thẳng:** Căng thẳng có thể làm cho triệu chứng viêm tuyến tiền liệt trở nên tồi tệ hơn. Thực hiện các phương pháp giảm căng thẳng như thiền, yoga hoặc liệu pháp hít thở sâu để giúp quản lý căng thẳng hiệu quả. 4. **Chăm sóc y tế định kỳ:** Theo dõi sức khỏe với các bác sĩ chuyên khoa là quan trọng để đảm bảo rằng tình trạng viêm tuyến tiền liệt được kiểm soát đúng cách. Trong một số trường hợp, bác sĩ có thể kê đơn thuốc hoặc liệu pháp điều trị phù hợp. 5. **Sử dụng sản phẩm bổ trợ theo hướng dẫn của bác sĩ:** Có nhiều sản phẩm bổ sung hoặc phương pháp điều trị tự nhiên có thể giúp giảm triệu chứng viêm tuyến tiền liệt, nhưng nên tham khảo ý kiến bác sĩ trước khi sử dụng. Bằng việc chú ý đến các biện pháp quản lý lối sống và chăm sóc dài hạn, người bệnh có thể sống chất lượng cuộc sống tốt hơn và giảm thiểu những tác động tiêu cực của viêm tuyến tiền liệt.